Shodan.io tips and tricks
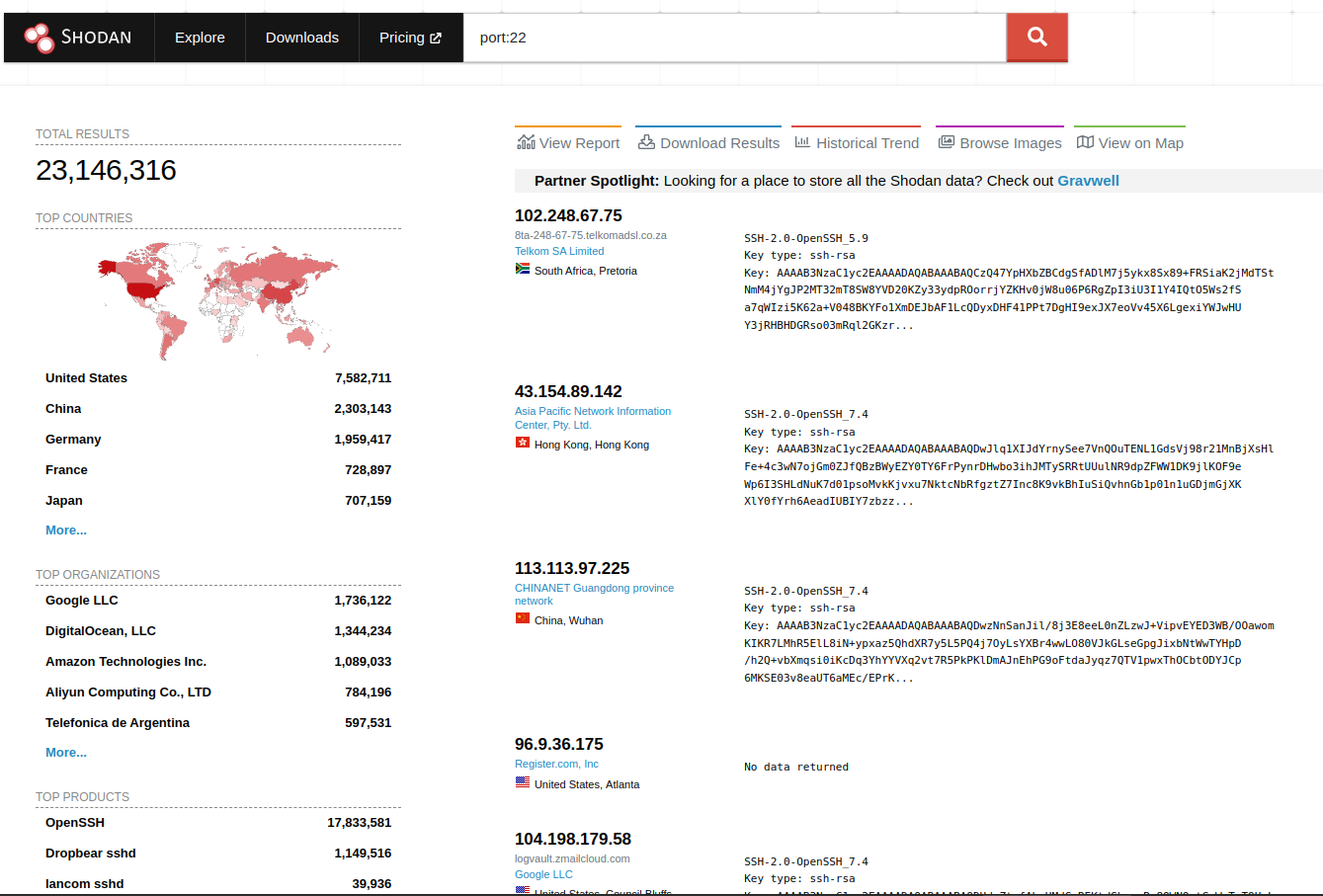
Shodan is a search engine for the internet of things (IoT). It allows users to search for specific types of internet-connected devices, such as security cameras or industrial control systems, and view information about them, such as their location, their internet protocol (IP) address, and their manufacturer.
This makes it a valuable tool for security researchers, who can use Shodan to identify vulnerable devices and track the spread of malware across the internet.
Shodan was created by John Matherly in 2009, and it has grown to become one of the most widely used search engines for IoT devices. One of the unique features of Shodan is its ability to search for specific keywords in the banners that many IoT devices send out over the internet. This allows users to search for devices using a variety of criteria, such as the type of device, its operating system, and its manufacturer.
In addition to its search capabilities, Shodan also offers a variety of other tools and services. For example, users can set up alerts to be notified when new devices matching their search criteria are added to the internet. They can also use Shodan to track the spread of malware across the internet, by searching for devices that have been infected with a specific strain of malware.
Overall, Shodan is an important tool for security researchers and others interested in the internet of things. It offers a unique way to search for and find internet-connected devices, and provides valuable information about those devices. While it does pose some risks, these are mitigated by the security measures in place to prevent abuse of the platform.
To use filters on Shodan, users first need to register for an account. Once they have done so, they can begin creating filters by clicking on the “Filters” tab on the left-hand side of the screen. This will bring up a list of available filters, which can be added to the search query by clicking on them.
Some examples of filters that can be used on Shodan include:
os:- This filter allows users to search for devices based on their operating system. For example, a search for os:linux will return results for devices running the Linux operating system.geo:- This filter allows users to search for devices based on their geographical location. For example, a search for geo:us will return results for devices located in the United States.hostname:- This filter allows users to search for devices based on their hostname, which is the name assigned to the device on the network. For example, a search for hostname:camera will return results for devices with “camera” in their hostname.
Once users have added filters to their search query, they can click the “Search” button to see the results. The results page will show a list of devices matching the search criteria, along with information about each device, such as its IP address and its location.
General Filters
| Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| after | Only show results after the given date (dd/mm/yyyy) string | string |
| asn | Autonomous system number string | string |
| before | Only show results before the given date (dd/mm/yyyy) string | string |
| category | Available categories: ics, malware string | string |
| city | Name of the city string | string |
| country | 2-letter country code string | string |
| geo | Accepts between 2 and 4 parameters. If 2 parameters: latitude,longitude. If 3 parameters: latitude,longitude,range. If 4 parameters: top left latitude, top left longitude, bottom right latitude, bottom right longitude. | string |
| hash | Hash of the data property integer | integer |
| has_ipv6 | True/ False boolean | boolean |
| has_screenshot | True/ False boolean | boolean |
| hostname | Full hostname for the device string | string |
| ip | Alias for net filter string | string |
| isp | ISP managing the netblock string | string |
| net | Network range in CIDR notation (ex. 199.4.1.0/24) string | string |
| org | Organization assigned the netblock string | string |
| os | Operating system string | string |
| port | Port number for the service integer | string |
| postal | Postal code (US-only) string | string |
| product | Name of the software/ product providing the banner string | string |
| region | Name of the region/ state string | string |
| state | Alias for region string | string |
| version | Version for the product string | string |
| vuln | CVE ID for a vulnerability string | string |
HTTP Filters
| Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| http.component | Name of web technology used on the website | string |
| http.component_category | Category of web components used on the website | string |
| http.html | HTML of web banners | string |
| http.html_hash | Hash of the website HTML | integer |
| http.status | Response status code | integer |
| http.title | Title for the web banners website | string |
NTP Filters
| Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| ntp.ip | IP addresses returned by monlist | string |
| ntp.ip_count | Number of IPs returned by initial monlist | integer |
| ntp.more | True/ False; whether there are more IP addresses to be gathered from monlist | boolean |
| ntp.port | Port used by IP addresses in monlist | integer |
SSL Filters
| Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| has_ssl | True / False | boolean |
| ssl | Search all SSL data | string |
| ssl.alpn | Application layer protocols such as HTTP/2 (“h2”) | string |
| ssl.chain_count | Number of certificates in the chain | integer |
| ssl.version | Possible values: SSLv2, SSLv3, TLSv1,TLSv1.1, TLSv1.2 | string |
| ssl.cert.alg | Certificate algorithm | string |
| ssl.cert.expired | True / False | boolean |
| ssl.cert.extension | vNames of extensions in the certificate | string |
| ssl.cert.serial | Serial number as an integer or hexadecimal string | integer / string |
| ssl.cert.pubkey.bits | Number of bits in the public key | integer |
| ssl.cert.pubkey.type | Public key type | string |
| ssl.cipher.version | SSL version of the preferred cipher | string |
| ssl.cipher.bits | Number of bits in the preferred cipher | integer |
| ssl.cipher.name | Name of the preferred cipher | string |
Telnet Filters
| Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| telnet.option | Search all the options | string |
| telnet.do | The server requests the client do support these options | string |
| telnet.don’t | The server requests the client to not support these options | string |
| telnet.will | The server supports these options | string |
| telnet.won’t | The server doesn’t support these options | string |
