Building a High-Performance Lock-Free Circuit Breaker in Go
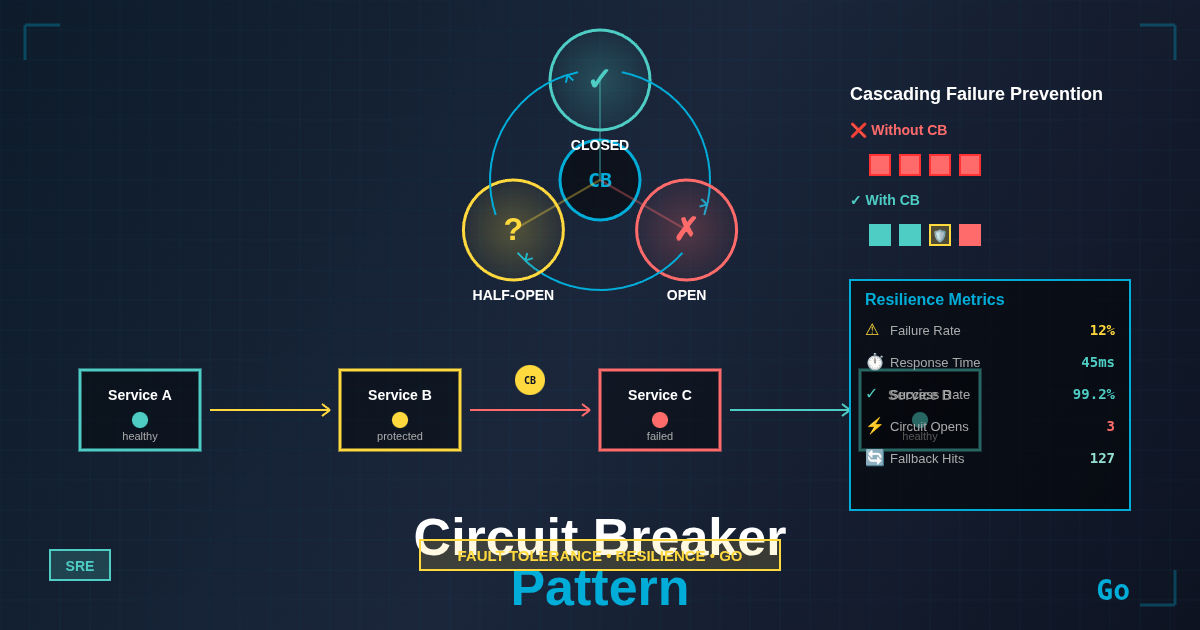
Introduction In distributed systems, cascading failures are one of the most devastating failure modes. When a downstream service becomes slow or unresponsive, upstream services can exhaust their resources waiting for responses, causing a domino effect that brings down entire systems. The 2017 AWS S3 outage, which cascaded across multiple services and lasted nearly four hours, demonstrated how a single service failure can ripple through interconnected systems.
Circuit breakers act as automatic safety switches that prevent cascading failures by detecting when a service is unhealthy and temporarily blocking requests to it.